A 2,000-year-old mechanical computer salvaged from a Roman shipwreck has astounded scientists who have finally unravelled the secrets of how the sophisticated device works.
The machine was lost among cargo in 65BC when the ship carrying it sank in 42m of water off the coast of the Greek island of Antikythera. By chance, in 1900, a sponge diver called Elias Stadiatos discovered the wreck and recovered statues and other artifacts from the site.
The machine first came to light when an archaeologist working on the recovered objects noticed that a lump of rock had a gear wheel embedded in it. Closer inspection of material brought up from the stricken ship subsequently revealed 80 pieces of gear wheels, dials, clock-like hands and a wooden and bronze casing bearing ancient Greek inscriptions.
Since its discovery, scientists have been trying to reconstruct the device, which is now known to be an astronomical calendar capable of tracking with remarkable precision the position of the sun, several heavenly bodies and the phases of the moon. Experts believe it to be the earliest-known device to use gear wheels and by far the most sophisticated object to be found from the ancient and medieval periods.
Using modern computer x-ray tomography and high resolution surface scanning, a team led by Mike Edmunds and Tony Freeth at Cardiff University peered inside fragments of the crust-encased mechanism and read the faintest inscriptions that once covered the outer casing of the machine. Detailed imaging of the mechanism suggests it dates back to 150-100 BC and had 37 gear wheels enabling it to follow the movements of the moon and the sun through the zodiac, predict eclipses and even recreate the irregular orbit of the moon. The motion, known as the first lunar anomaly, was developed by the astronomer Hipparcus of Rhodes in the 2nd century BC, and he may have been consulted in the machine's construction, the scientists speculate.
Remarkably, scans showed the device uses a differential gear, which was previously believed to have been invented in the 16th century. The level of miniaturisation and complexity of its parts is comparable to that of 18th century clocks.
Some researchers believe the machine, known as the Antikythera Mechanism, may have been among other treasure looted from Rhodes that was en route to Rome for a celebration staged by Julius Caesar.
One of the remaining mysteries is why the Greek technology invented for the machine seemed to disappear. No other civilisation is believed to have created anything as complex for another 1,000 years. One explanation could be that bronze was often recycled in the period the device was made, so many artefacts from that time have long ago been melted down and erased from the archaelogical record. The fateful sinking of the ship carrying the Antikythera Mechanism may have inadvertently preserved it. "This device is extraordinary, the only thing of its kind," said Professor Edmunds. "The astronomy is exactly right ... in terms of historic and scarcity value, I have to regard this mechanism as being more valuable than the Mona Lisa." The research, which appears in the journal Nature today, was carried out with scientists at the National Archaeological Museum of Athens where the mechanism is held and the universities of Athens and Thessaloniki.
Sphere: Related Content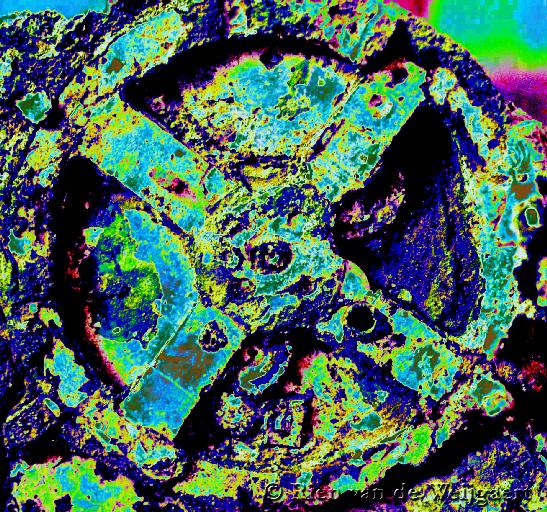




No comments:
Post a Comment